As many readers are no doubt aware, the FOSDEM 2012 conference is taking place this weekend in Brussels. This year I was organized enough to submit a proposal for a talk and was very happy to be accepted. My talk is titled “Building app sandboxes on top of LXC and KVM with libvirt” and is part of the Virtualization & Cloud Dev Room. As you can guess from the title, I will be talking in some detail about the libvirt-sandbox project I recently announced. Richard Jones is also attending to provide a talk on libguestfs and how it is used in cloud projects like OpenStack. There will be three talks covering different aspects of the oVirt project, a general project overview, technical look at the management engine and a technical look at the node agent VDSM. Finally the GNOME Boxes project I mentioned a few weeks ago will also be represented in the CrossDesktop devroom.
Besides these virtualization related speakers, there are a great many other Red Hat people attending FOSDEM this year, so we put together a small flyer highlighting all their talks. In keeping with the spirit of FOSDEM, these talks will of course be community / technically focused, not corporate marketing ware :-) I look forward to meeting many people at FOSDEM this year, and if all goes well, make it a regular conference to attend.
I have mentioned in passing every now & then over the past few months, that I have been working on a tool for creating application sandboxes using libvirt, LXC and KVM. Last Thursday, I finally got around to creating a first public release of a package that is now called libvirt-sandbox. Before continuing it is probably worth defining what I consider the term “application sandbox” to mean. My working definition is that an “application sandbox” is simply a way to confine the execution environment of an application, limiting the access it has to OS resources. To me one notable point is that there is no need for a separate / special installation of the application to be confined. An application sandbox ought to be able to run any existing application installed in the OS.
Background motivation & prototype
For a few Fedora releases, users have had the SELinux sandbox command which will execute a command with a strictly confined SELinux context applied. It is also able to make limited use of the kernel filesystem namespace feature, to allow changes to the mount table inside the sandbox. For example, the common case is to put in place a different $HOME. The SELinux sandbox has been quite effective, but there is a limit to what can be done with SELinux policy alone, as evidenced by the need to create a setuid helper to enable use of the kernel namespace feature. Architecturally this gets even more problematic as new feature requests need to be dealt with.
As most readers are no doubt aware, libvirt provides a virtualization management API, with support for a wide variety of virtualization technologies. The KVM driver is easily the most advanced and actively developed driver for libvirt with a very wide array of features for machine based virtualization. In terms of container based virtualization, the LXC driver is the most advanced driver in libvirt, often getting new features “for free” since it shares alot of code with the KVM driver, in particular anything cgroup based. The LXC driver has always had the ability to pass arbitrary host filesystems through to the container, and the KVM driver gained similar capabilities last year with the inclusion of support for virtio 9p filesystems. One of the well known security features in libvirt is sVirt, which leverages MAC technology like SELinux to strictly confine the execution environment of QEMU. This has also now been adapted to work for the LXC driver.
Looking at the architecture of the SELinux sandbox command last year, it occurred to me that the core concepts mapped very well to the host filesystem passthrough & sVirt features in libvirt’s KVM & LXC drivers. In other words, it ought to be possible to create application sandboxes using the libvirt API and suitably advanced drivers like KVM or LXC. A few weeks hacking resulted in a proof of concept tool virt-sandbox which can run simple commands in sandboxes built on LXC or KVM.
The libvirt-sandbox API
A command line tool for running applications inside a sandbox is great, but even more useful would be an API for creating application sandboxes that programmers can use directly. While libvirt provides an API that is portable across different virtualization technologies, it cannot magically hide the differences in feature set or architecture between the technologies. Thus the decision was taken to create a new library called libvirt-sandbox that provides a higher level API for managing application sandboxes, built on top of libvirt. The virt-sandbox command from the proof of concept would then be re-implemented using this library API.
The libvirt-sandbox library is built using GObject to enable it to be accessible to any programming language via GObject Introspection. The basic idea is that programmer simply defines the desired characteristics of the sandbox, such as the command to be executed, any arguments, filesystems to be exposed from host, any bind mounts, private networking configuration, etc. From this configuration description, libvirt-sandbox will decide upon & construct a libvirt guest XML configuration that can actually provided the requested characteristics. In other words, the libvirt-sandbox API is providing a layer of policy avoid libvirt, to isolate the application developer from the implementation details of the underlying hypervisor.
Building sandboxes using LXC is quite straightforward, since application confinement is a core competency of LXC. Thus I will move straight to the KVM implementation, which is where the real fun is. Booting up an entire virtual machine probably sounds like quite a slow process, but it really need not be particularly if you have a well constrained hardware definition which avoids any need for probing. People also generally assume that running a KVM guest, means having a guest operating system install. This is absolutely something that is not acceptable for application sandboxing, and indeed not actually necessary. In a nutshell, libvirt-sandbox creates a new initrd image containing a custom init binary. This init binary simply loads the virtio-9p kernel module and then mounts the host OS’ root filesystem as the guest’s root filesystem, readonly of course. It then hands off to a second boot strap process which runs the desired application binary and forwards I/O back to the host OS, until the sandboxed application exits. Finally the init process powers off the virtual machine. To get an idea of the overhead, the /bin/false binary can be executed inside a KVM sandbox with an overall execution time of 4 seconds. That is the total time for libvirt to start QEMU, QEMU to run its BIOS, the BIOS to load the kernel + initrd, the kenrel to boot up, /bin/false to run, and the kernel to shutdown & QEMU to exit. I think 3 seconds is pretty impressive todo all that. This is a constant overhead, so for a long running command like an MP3 encoder, it disappears into the background noise. With sufficient optimization, I’m fairly sure we could get the overhead down to approx 2 seconds.
Using the virt-sandbox command
The Fedora review of the libvirt-sandbox package was nice & straightforward, so the package is already available in rawhide for ready to test the VirtSandbox F17 feature. The virt-sandbox command is provided by the libvirt-sandbox RPM package
# yum install libvirt-sandbox
Assuming libvirt is already installed & able to run either LXC or KVM guests, everything is ready to use immediately.
A first example is to run the ‘/bin/date’ command inside a KVM sandbox:
$ virt-sandbox -c qemu:///session /bin/date
Thu Jan 12 22:30:03 GMT 2012
You want proof that this really is running an entire KVM guest ? How about looking at the /proc/cpuinfo contents:
$ virt-sandbox -c qemu:///session /bin/cat /proc/cpuinfo
processor : 0
vendor_id : GenuineIntel
cpu family : 6
model : 2
model name : QEMU Virtual CPU version 1.0
stepping : 3
cpu MHz : 2793.084
cache size : 4096 KB
fpu : yes
fpu_exception : yes
cpuid level : 4
wp : yes
flags : fpu de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pse36 clflush mmx fxsr sse sse2 syscall nx lm up rep_good nopl pni cx16 hypervisor lahf_lm
bogomips : 5586.16
clflush size : 64
cache_alignment : 64
address sizes : 40 bits physical, 48 bits virtual
power management:
How about using LXC instead of KVM, and providing an interactive console instead of just a one-shot command ? Yes, we can do that too:
$ virt-sandbox -c lxc:/// /bin/sh
sh-4.2$ ps -axuwf
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
root 1 0.0 0.0 165436 3756 pts/0 Ss+ 22:31 0:00 libvirt-sandbox-init-lxc
berrange 24 0.0 0.1 167680 4688 pts/0 S+ 22:31 0:00 libvirt-sandbox-init-common
berrange 47 0.0 0.0 13852 1608 pts/1 Ss 22:31 0:00 \_ /bin/sh
berrange 48 0.0 0.0 13124 996 pts/1 R+ 22:31 0:00 \_ ps -axuwf
Notice how we only see the processes from our sandbox, none from the host OS. There are many more examples I’d like to illustrate, but this post is already far too long.
Future development
This blog post might give the impression that every is complete & operational, but that is far from the truth. This is only the bare minimum functionality to enable some real world usage. Things that are yet to be dealt with include
- Write suitable SELinux policy extensions to allow KVM to access host OS filesystems in readonly mode. Currently you need to run in permissive mode which is obviously something that needs solving before F17
- Turn the virt-viewer command code for SPICE/VNC into a formal API and use that to provide a graphical sandbox running Xorg.
- Integrate a tool that is able to automatically create sandbox instances for system services like apache to facilitate confined vhosting deployments
- Correctly propagate exit status from the sandboxed command to the host OS
- Unentangle stderr and stdout from the sandboxed command
- Figure out how to make dhclient work nicely when / is readonly and resolv.conf must be updated in-place
- Expose all the libvirt performance tuning controls to allow disk / net I/O controls, CPU scheduling, NUMA affinity, etc
- Wire up libvirt’s firewall capability to allow detailed filtering of network traffic to/from sandboxes
- Much more…
For those attending FOSDEM this year, I will be giving a presentation about libvirt-sandbox in the virt/cloud track.
Oh and as well as the released tar.gz mentioned in the first paragraph, or the Fedora RPM, the code is all available in GIT
In the five years since the libvirt project started, alot has changed. The size of the libvirt API has increased dramatically; the number of languages you can access the API from has likewise grown to cover most important targets; libvirt has been translated to fit into several other object models; plugins have been developed to bind libvirt to other tools. At the same time many other libraries have grown up alongside libvirt, not least libguestfs, gtk-vnc and more recently spice-gtk. Together all these pieces provide a rich software development platform for people building virtualization management applications. A picture is worth 1000 words, so to keep this blog post short, here is the way I visualize the pieces in the virtualization tools platform, and a selection of the applications built on it (click to enlarge the image)
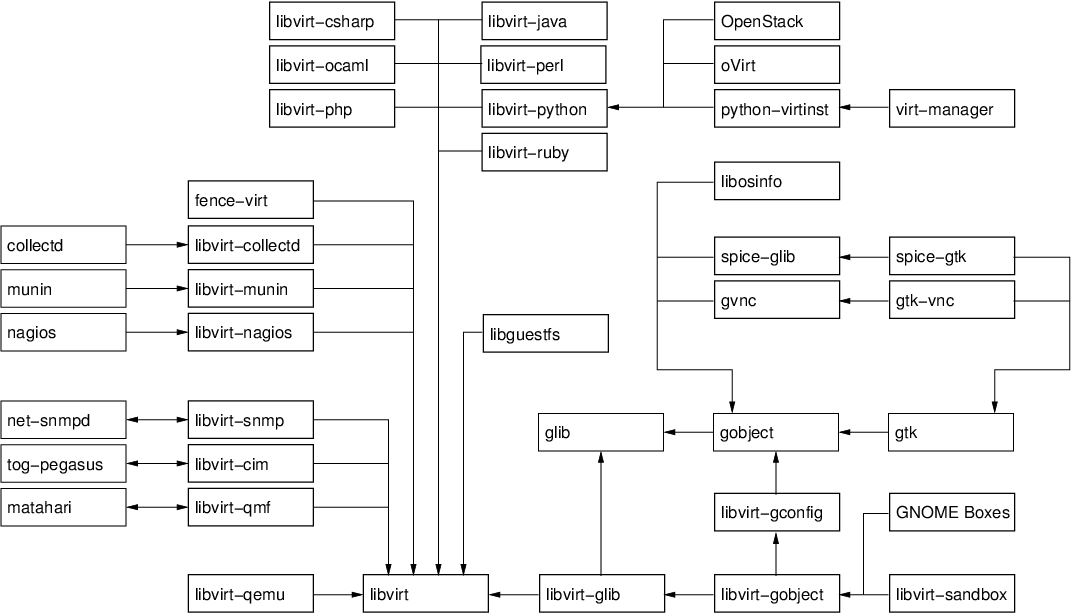
The base layer
- libvirt: the core hypervisor agnostic management API, coring virtual machines, host devices, networking, storage, security and more
- libvirt-qemu: a small set of QEMU specific APIs, such as the ability to talk to the QEMU monitor, or attach to externally launched QEMU guests. This library builds on top libvirt.
- libguestfs: the library for manipulating and accessing the contents of guest filesystem images. This uses libvirt for some actions internally. libguestfs has its own huge set of language bindings which are not shown in the diagram, for the sake of clarity. It will also soon be gaining a mapping into the GObject type system, which will help it play nicely with other GObject based APIs here.
Language bindings
The language bindings for libvirt aim to be a 1-for-1 export of the libvirt C API into the corresponding language. They generally don’t attempt to change the way the libvirt API looks or is structured. There is generally completely interoperability between all language bindings, so you can trivially have part of your application written in Perl and another part written in Java and play nicely together.
- libvirt-ocaml: a binding into the OCaml functional language
- libvirt-php: a binding into the PHP scripting language
- libvirt-perl: a binding into the Perl scripting language
- libvirt-python: a binding into the Python scripting language, which comes as a standard part of the libvirt package
- libvirt-java: a binding into the Java object language
- libvirt-ruby: a binding into the Ruby scripting language
- libvirt-csharp: a binding into the C# object language
Object mappings
The object mappings are distinct from language bindings, because they will often significantly change the structure of the libvirt API to fit in the requirement of the object system being targeted. Depending on the object systems involved, this translation might be lossless, thus an application generally has to pick one object system & stick with it. It is not a good idea to do a mixture of SNMP and QMF calls from the same application.
- libvirt-snmp: an agent for SNMP that translates from an SNMP MIB to libvirt API calls.
- libvirt-cim: an agent for CIM the translates from the DMTF virtualization schema to the libvirt API
- libvirt-qmf: an agent for Matahari that translates from a QMF schema to the libvirt API
Infrastructure plugins
Many common infrastructure applications can be extended by adding plugins for new functionality. This particularly common with network monitoring or performance collection applications. libvirt can of course be used to create plugins for such applications
- libvirt-collectd: a plugin for collectd that reports statistics on virtual machines
- libvirt-munin: a plugin for collectd that reports statistics on virtual machines
- libvirt-nagios: a plugin for nagious that reports where virtual machines are running
- fence-virt: a plugin for clustering software to allow virtual machines to be “fenced”
GObject layer
The development of a set of GObject based libraries came about after noticing that many users of the basic libvirt API were having to solve similar problems over & over. For example, every application wanted some programmatic way to extract info from XML documents. Many applications wanted libvirt translated into GObjects. Many applications needed a way to determine optimal hardware configuration for operating systems. The primary reasons for choosing to use GObject as the basis for these APIs was first to facilitate development of graphical desktop applications. With the advent of GObject Introspection, the even more compelling reason is that you get language bindings to all GObject libraries for free. Contrary to popular understanding, GObject is not solely for GTK based desktop applications. It is entirely independent of GTK and can be easily used from any conceivable application. If libvirt were to be started from scratch again today, it would probably go straight for GObject as the basis for the primary C library. It is that compelling.
- libosinfo: an API for managing metadata related to operating systems. It includes a database of operating systems with details such as common download URLs, magic byte sequences to identify ISO images, lists of supported hardware. In addition there is a database of hypervisors and their supported hardware. The API allows applications to determine the optimal virtual hardware configuration for deployment of an operating system on a particular hypervisor.
- gvnc: an API providing a client for the RFB protocol, used for VNC servers. The API facilitates the creation of new VNC client applications.
- spice–glib: an API providing a client for the SPICE protocol, used for SPICE servers. The API facilitates the creation of new SPICE client applications.
- libvirt-glib: an API binding the libvirt event loop into the GLib main loop, and translating libvirt errors into GLib errors.
- libvirt-gconfig: an API for generating and manipulating libvirt XML documents. It removes the need for application programmers to directly deal with raw XML themselves.
- libvirt-gobject: an API which translates the libvirt object model, also integrating them with the lbivirt-gconfig APIs.
- libvirt-sandbox: an API for building application sandboxes using virtualization technology.
GTK layer
- gtk-vnc: an API building on gvnc providing a GTK widget which acts as a VNC client. This is used in both virt-manager & virt-viewer
- spice-gtk: an API building on spice-glib providing a GTK widget which acts as a SPICE client. This is used in both virt-manager & virt-viewer
Applications
- python-virtinst: provides the original python virt-install command line tool, as well as a python API which is leveraged by virt-manager. The python-virtinst internal API was the motivation behind the libosinfo library and libvirt-gconfig library
- virt-manager: provides a general purpose desktop application for interacting with libvirt managed virtualization hosts. The virt-manager internal API was the motivation behind the libvirt-gobject library
- oVirt: the umbrella project for building an open source virtualized data center management application. Its VDSM component uses the libvirt python language bindings for managing KVM hosts
- OpenStack: the umbrella project for building an open source cloud management application. Its Nova component uses the libvirt python language bindings for managing KVM, Xen and LXC hosts.
- GNOME Boxes: the new GNOME desktop application for running virtual machines and accessing remote desktops. It uses libirt-gobject, libosinfo, gtk-vnc & spice-gtk via automatically generated vala bindings.
The Future
- Get oVirt, OpenStack, python-virtinst and virt-manager using the libosinfo library to centralize definitions of what hardware config to use for deploying operating systems
- Get oVirt & OpenStack using the libvirt-gconfig library to generate configuration, instead of building XML documents up through string concatenation
- Convert python-virtinst & virt-manager to use the libvirt-gconfig, libvirt-gobject libraries instead of their private internal equivalents
- Create a remote-viewer library which pulls in both gtk-vnc and spice-gtk in a higher level framework. This is essentially pulling the commonality out of virt-viewer, virt-manager and GNOME boxes use of gtk-vnc and spice-gtk.
- Create a libvirt-install library which provides APIs for provisioning operating systems. This would be pulling out commonality between the way python-virtinst, GNOME boxes and other applications deploy new operating systems. This would be a bridge layer between libosinfo and libvirt-gobject
There is undoubtably plenty of stuff I left out of this diagram & description. For example there are many other data center & cloud management projects that are based on libvirt, which I left out for clarity. There are plenty more libvirt plugins for other applications too, many I will never have heard about. No doubt our future plans will change too, as we adapt to new information. This should have given a good overview of how broad the open source virtualization tools software development ecosystem has become.
